Bronchitis
Bronchitis is a disease that is characterized by a severe inflammation of the main air passages that stem from the lungs. There are two different types of bronchitis, one being acute (short-lived) and the other lasting a long time and often reoccurring or chronic.
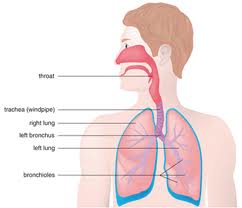
Alternative Names for Bronchitis
Other names for bronchitis include Acute Bronchitis, Chronic Bronchitis, and Industrial Bronchitis. These are all distinct forms of bronchitis and are treated differently and caused by different circumstances.
Symptoms of Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis usually subsides within 7 to 10 days.
Acute bronchitis usually consists of a lingering cough and is accompanied by the following symptoms
- Shortness of breath, especially following physical activities
- Wheezing
- Difficulty breathing normally
- Clear, white, or yellowish mucus that is released during coughs
- Extreme discomfort in the internal chest region
Chronic bronchitis is very similar to acute bronchitis in that the symptoms are almost identical. The biggest difference between chronic bronchitis and acute bronchitis is that chronic bronchitis tends to linger for long periods of time or have a recurring affect.
Industrial bronchitis also exhibits the same types of symptoms but is characterized by its cause. Industrial bronchitis can be the result from prolonged exposure to chemicals, fumes, dusts, gas, and other dangerous substances.
Bronchitis? Get Remedies Fast!
High fevers may also accompany the bronchitis virus and can reach up to 101 to 102 degrees Fahrenheit. While a high fever may be present, it is not always a sign of bronchitis. Fevers can cause the body to feel tired throughout the day. Another common symptom of acute bronchitis is a feeling of tightness, pain, or burning throughout the chest region. This pain may become worse when the patient coughs or takes a deep breath.
Resulting Conditions
It can be difficult to tell the difference between the symptoms that are associated with acute bronchitis and other diseases such as pneumonia and asthma.
While bronchitis may not be considered a serious illness, pneumonia and asthma can be deadly. For this reason, it is important to see a physician who can properly diagnose these symptoms as being either acute bronchitis or some other illness. If you or a family member is experiencing more than one of these systems it is important to receive proper medical care.
Causes of Bronchitis
The leading cause of chronic bronchitis is smoking. Extensive smoking exposes the body to dangerous chemicals found in cigarettes and other forms of tobacco. These chemicals and substances cause a severe irritation in the bronchial tubes which can lead to chronic bronchitis. Second-hand smoke is also a factor in determining whether or not you are at risk of chronic bronchitis.
Most forms of acute bronchitis is caused by an infection of the epithelium of the bronchi due to exposure to a virus. A common form of the bronchitis virus that affects infants is known as Respiratory Syncytial Viruses, or RSV.
Bronchitis is contagious and parents are advised to keep their children indoors and home from school until the virus is destroyed. This act will protect other children from being exposed to the highly contagious bronchitis virus.
Bacteria and chemicals are also known causes of bronchitis. Bronchitis most often occurs during flu and cold season due to the environment which allows bronchitis viruses to survive.
Risk Factors of Bronchitis
Because smoking is one of the leading causes of bronchitis, people who smoke or chew tobacco are at the greatest risk.
People who have a history of asthmatic and other respiratory problems are also at a higher risk of bronchitis.
Elderly people, infants, and small children tend to be at a much higher risk for acute bronchitis than young adults and teenagers.
This trend is due to the weaker immune systems of people within the more susceptible age groups.
Chronic bronchitis is not typically found in young children, but is most common in adults over the age of 45.
Women have been shown to be at a much higher risk for chronic bronchitis than men.
Women account for over two times as many chronic bronchitis cases than men.
Existing lung diseases greatly increase the risk of a person to catch the bronchitis virus. These lung diseases can include conditions such as asthma and trouble breathing.
Factory employees who work closely with dangerous chemicals, asbestos, carbon dioxide, dusts and other harmful substances are also at an increased risk of attracting the industrial bronchitis virus. Industrial bronchitis is also more prevalent in large cities where air pollution, allergies, and infections are more common.
Prevention Tips Against Bronchitis
Environment and lifestyle tend to be the greatest causes of bronchitis. For this reason, there are many preventative measures that can be taken to protect ourselves against the viral disease.
The following are a few suggestions to prevent bronchitis
- Avoid the spread of the virus by avoiding people with colds. It is common knowledge that the less you are exposed to a virus or disease, the greater the chance you will have of avoiding the disease altogether.
- Get vaccinated. By receiving an annual flu vaccine you will be able to protect yourself from getting influenza, or the flu. Many cases of bronchitis stem from cases of the flue, so by reducing your chances of getting the flu you are also reducing the risk of bronchitis.
- Avoid smoking. This preventative measure includes avoiding secondhand smoke. Tobacco is one of the greatest causes of bronchitis and other diseases. Not only will you be protecting yourself from getting the virus, but you will also be protecting your children and family members.
- Regularly wash your hands. One of the best ways to prevent catching a viral infection is to have good hygiene. Good hygiene includes a frequent washing of the hands and the use of an effective hand sanitizer. Even when practicing this good hygiene it is important to avoid excessive rubbing of the nose and eyes.
- Wear a mask during flu season. When a large flu epidemic breaks out, it is important to have access to simple face masks that will prevent the spread of disease.
- Take vitamins regularly. By taking a daily vitamin and ensuring proper nutrition, the body’s immune system will be able to more effectively combat any external predators to the respiratory system. Proper health is the best protection against all vitamins.
- Perform regular exercise. Similar to taking daily vitamins, the habit of regular exercise will protect your body from unwanted diseases, viruses, and illness. It is important to set up a regular plan of exercise in order to protect your respiratory system from the attack of a bronchitis virus.
Tests and Diagnosis Considerations for Bronchitis
Most family and general practitioners will have the machines necessary in order to determine if you are infected with the bronchitis virus. If they are unable to determine the cause of the symptoms, he or she may refer you to a pulmonologist for further diagnosis.
There are a few tests that a physician will perform in order to determine if you have bronchitis. Most doctors will assume that if there is not a cough associated with the sickness that bronchitis is not the issue. However, they may deem it necessary to perform the tests even without the accompaniment of a cough.
The first test most physicians will perform is to listen for wheezing and other sounds within your lungs that are not normal. This is done using a standard stethoscope, similar to those used to hear a heart beat.
An x-ray is also important in order to rule out cases such as pneumonia. Physicians will take a sample of mucus from the throat in order to detect the presence of unwanted bacteria or the flu virus. You may also undergo certain blood tests and possibly a pulmonary function test in order to rule out other diseases such as lung cancer or pneumonia. If your physician determines that you may be afflicted with some other disease, he or she may refer you to a specialist in order to receive further diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment Options for Bronchitis
Herbal and Home Remedies
There are several methods of treating bronchitis at home, but if the symptoms do not subside within a few days it should be recommended to visit with a physician. One of the most common ways to recover from bronchitis is to drink lots of hot fluids, such as herbal teas, to wash away and clean out the infected mucus. Many vegetables such as peppers and onions have anti-pyretic and expectorant properties which are effective in combating fevers and other symptoms of bronchitis.
Herbal supplements such as Echinacea and astragalus are commonly known to be antivirals, meaning they can fight existing viruses within the body and also protect against unwanted viruses. Other herbs such as pau d’arco, reishi, and maitake mushrooms are also taken in addition to other herbs to combat acute and chronic bronchitis.
Vitamins are among the most important supplements in warding off the bronchitis virus. Vitamin C is an especially effective antiviral. Antioxidants, Vitamin A, and flavonoids are also vital to the bodies antiviral immune system.
Because most of these herbs and vitamins are natural, there are no significant risks associated with them.
Pharmaceutical Treatments
Antibiotics are typically used to kill or stop the growth of a dangerous type of bacteria. They are only taken if the patient has no other significant health problems. For acute bronchitis, most scientists recommend that antibiotics are not take.
Acute bronchitis patients are typically told to get plenty of rest and drink lots of fluids. This process will typically kill the virus or flush it out of the body’s system. However, if the bronchitis becomes chronic or is causes by industrial activities such as gas or chemicals, antibiotics can be prescribed in order to prevent other disease, such as lung disease, from becoming present.
Although prescription drugs have not been proven to significantly help in the fight against bronchitis, your doctor may prescribe a type of medicine called a bronchodilator. The purpose of this treatment is to dilate the patients airways and allow the lungs to transport air more easily.
A bronchodilator is not taken as a pill or liquid drug, but is rather inhaled through a machine. The inhaler is similar to those used by people with sever asthma.
If chronic bronchitis does not subside within a few months, your physician may require that you take steroids. Though steroids prevent some slight health hazards, they will allow your body’s immune system to get the nourishment it needs and hopefully kill off the bronchitis virus.
Surgical Treatments
There is no known surgical operation that successfully treats bronchitis. However, if you happen to be preparing for some other type of surgery and experience symptoms of bronchitis it is important to alert your surgeon. Bronchitis patients have been known to react poorly to surgical anesthetics.

No Comments