High Cholesterol
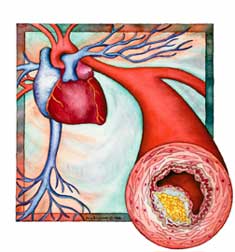
Cholesterol is a fat-like substance that can build up along the walls of one’s arteries, causing atherosclerosis.
If the arteries become blocked or narrowed by excess cholesterol, or plaque, the blood cannot transport the required oxygen to the heart or brain, resulting in heart attack or stroke. Having high cholesterol increases one’s chance of having heart disease.
Understanding Cholesterol
Cholesterol can be broken down into four parts: Total Cholesterol, LDL (bad cholesterol), HDL (good cholesterol), and Triglycerides.
LDL cholesterol is known as bad cholesterol because it is the cause of buildup and blockage of the arteries.
High Cholesterol? Get Remedies Fast!
HDL is considered good cholesterol because it aids in lowering cholesterol buildup in the arteries. Triglycerides are a form of fat found in the blood, and if in excess can result in hypertriglyceridemia, which is linked to coronary artery disease.
Understanding one’s cholesterol numbers is important in maintaining a healthy heart. Desirable Total Cholesterol range is below 200 mg/dL ( below 5.2 mmol/L). LDL levels are desirable below 100 mg/dL ( 2.6 mmol/L). Since HDL is the good cholesterol, the numbers should be high. The ideal numbers should be 60 mg/dL (1.5 mmol/L) or higher to lower the risk for heart disease.
A desirable level for Triglycerides should be below 150 mg/dL (below 1.7 mmol/L).
Alternative Names for High Blood Cholesterol
Other names which are used for high blood cholesterol include hypercholesterolemia, which means high blood cholesterol; hyperlipidemia, which means increased levels of lipids; and hyperlipoproteinemia, which is elevated levels of lipoproteins.
Symptoms of High Blood Cholesterol
High blood cholesterol can oftentimes go unnoticed until one has the proper blood testing done to discover it. Certain conditions may occur which may cause one to get tested such as xanthoma (cholesterol patches on the skin), xanthelasma palpabrum (yellow patches around the eyelids), or arcus senilis (white discoloration of the cornea). These are all due to elevated levels in cholesterol.
Cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease all result from hypercholesterolemia.
Causes
There are many causes for having high cholesterol, with some things being controllable and some not. The causes which can be controlled include diet, weight, and physical activity. Those which cannot be controlled include age, gender, and heredity.
Other contributors may include diabetes mellitus, kidney disease, hypothyroidism, Cushing’s syndrome, anorexia, and lack of sleep.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for high blood cholesterol include high blood pressure and low HDL cholesterol. This can be monitored and treated with medications.
For those with a family history of early heart disease, there should be an awareness of the potential medical condition and the appropriate precautions should be taken.
Age is also a risk factor (men 45 or older and women 55 or older) and tests should be done on a regular basis.
Smoking causes damage to the arteries which enable them to easily accumulate fatty deposits. It also lowers the level of HDL cholesterol. This is a risk factor that can be controlled by quitting smoking.
Being obese, with a body mass index of 30 or higher, also puts one at risk for heart disease. Diet and exercise is extremely important and can be controlled. Diets which contain red meat and fat dairy products; saturated fats, found in animal products; and trans fats, found in items such as cookies, crackers, and cakes, can all lead to high cholesterol levels.
Prevention Tips
Prevention of high blood cholesterol mainly includes a change of lifestyle habits, and this includes diet and exercise.
Diet
Being obese can increase cholesterol and it only makes sense that if one loses weight, the total cholesterol level will come down. This can be done by consuming a healthy diet rich in fiber by eating foods such as oatmeal, oat bran, and other high fiber foods like kidney beans, prunes, apples, barley, and pears. One should avoid trans fats and saturated fats by replacing them with monounsaturated fats. Monounsaturated fat can be found in olive oil, canola oil, and peanut oil.
Eating fish is good for a heart healthy diet because it contains omega-3 fatty acids. These fatty acids can help reduce blood pressure and prevent the risk of blood clots.
The fish with the highest levels of omega-3 fatty acids include mackerel, lake trout, herring, sardines, tuna, salmon, and halibut. It is recommended that one eat two servings of fish a week, preferably baked or grilled. If fish is unavailable, omega-3 fatty acids can be found in ground flaxseed, canola oil, and supplements.
Nut Benefits
Nuts are a good source of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The best ones to eat are almonds, walnuts, hazelnuts, pecans, peanuts, and pistachios. It is recommended to eat only a handful of nuts per day, as they are high in calories, to help reduce the risk of heart disease.
Other Diet Changes
Other changes to the diet can include adding olive oil and foods with added plant sterols or stanols to the diet. Olive oil can lower the LDL and leave the HDL alone because it contains a mix of antioxidants. It is recommended to use about 2 tablespoons of olive oil a day to achieve a healthy heart.
Many foods now have added plant sterols and stanols which can block the absorption of LDL cholesterol without affecting the triglyceride or HDL levels. Such foods include yogurt drinks, orange juice, and margarines.
Exercise
Regular exercise is essential in maintaining a healthy heart. Try working out for at least 30 minutes a day by walking, running, bike riding, or aerobics. Try alternating activities to keep from getting bored or find a partner to work out with. Involve family members by doing physical activities together, thus creating quality family time.
Smoking
Avoid smoking. If one does smoke, quitting can do wonders to increase the HDL levels.
Tests and Diagnosis Considerations
Cholesterol screenings should be checked on an average at least every 5 years for adults. Blood tests are the type of tests performed to determine one’s cholesterol levels. A lipoprotein profile is one such test. This requires a 9-12 hour fast.
This test will report the total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides.
Patients who are already on medication for cholesterol may be tested more frequently to monitor how well the drug is working. This is also the case for those with high risk factors such as cigarette smoking, age of the individual, hypertension, family history of heart disease, those already suffering a heart attack, or those with diabetes mellitus.
Treatment Options

Lifestyle changes such as diet control and exercise are the first treatment options to consider.
If the blood cholesterol still remains high, there are other alternatives to consider, such as herbal remedies or medications.
Herbal and Home Remedies
There are a few natural products and supplements which may help in reducing cholesterol.
Some to consider trying are artichokes, barley, beta-sitosterol, blond psyllium, garlic, oat bran, and sitostanol. One should always let the doctor be aware of the cholesterol-lowering supplements that are being taken.
Barley may reduce the total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol. It is recommended to take 3 grams of barley oil extract or 30 grams of barley bran flour a day. There doesn’t seem to be any side effects with taking barley.
Artichoke extract may help in reducing the total cholesterol and LDL. It is recommended to take 1,800 to 1,920 mg a day, divided into 2 or 3 doses. Side effects may include gas or allergic reactions.
Reducing Total Cholesterol
Beta-sitosterol may reduce total cholesterol and LDL. It is recommended to take 800 mg to 6 grams a day, divided and taken before meals, or 2 tablespoons of margarine containing beta-sitosterol a day. Side effects may include nausea, indigestion, gas, diarrhea, or constipation.
Blond psyllium is found in seed husks and Metamucil-type products. This may reduce the total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol. It is recommended to take 5 gm seed husk twice a day or 1 serving a day of Metamuci-type products. Side effects may include gas, stomach pain, diarrhea, or constipation.
Fish Products
Fish oil can be found as liquid oil or in oil-filled caplets. It may reduce triglycerides. The side effects include bad breath, fish taste, gas, nausea or diarrhea. It may also react with some blood-thinning medications. It is recommended to take 2 to 5 grams a day.
Ground flaxseed may reduce total triglycerides. It is recommended to take 40-50 grams a day mixed with cereal or yogurt. It may cause gas or diarrhea and may interact with blood-thinning medications.
Garlic & Other Remedies
Garlic extract may reduce total cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides. It is recommended to take 600 to 1200 mg a day, divided into 3 separate doses. Side effects may include bad breath or body odor, heartburn, gas, or vomiting. It may also interfere with blood-thinning medications.
Oat bran is found in oatmeal and whole oats. It is recommended to take up to 150 grams of whole-oat products daily. It may cause gas or bloating.
Sitostanol is found in oral supplements and some margarines. It may help in reducing total cholesterol and LDL. It is recommended to take 300 mg to 4 g daily or 4 ½ teaspoons of margarine containing sitostanol a day. Side effects may include diarrhea.
Pharmaceutical
Drug treatment for reducing high cholesterol comes in the form of statins, bile acid resins, nicotinic acid, fibric acids, and cholesterol absorption inhibitors. Many doctors prescribe medications to use in addition to diet and exercise.
Statins are the most common medications used to treat cholesterol. They block a substance the liver needs to produce cholesterol and they also help the body absorb cholesterol, thereby decreasing LDL and triglycerides and slightly increasing HDL.
Statin medications include Lipitor (atorvastatin), Lescol (fluvastatin), Altoprev (lovastatin), Mevacor (lovastatin), Pravachol (pravastatin), Crestor (rosuvastatin), and Zocor (simvastatin). Possible side effects include nausea, stomach pain, constipation, diarrhea, muscle soreness, cramps, pain, and weakness.
Bile Acids
Bile-acid-binding resins lower cholesterol by binding to bile acids. This then makes the liver use the excess cholesterol to make more bile acids. This will help in reducing the LDL cholesterol level in the blood.
Medications include Questran (cholestyramine), Welchol (colesevelam), and Colestid (colestipol). Possible side effects include constipation, nausea, bloating, gas, and an increase in triglycerides.
Dietary Cholesterol
Cholesterol absorption inhibitors limit the absorption of dietary cholesterol, reducing the amount of LDL blood cholesterol and triglycerides, and increasing HDL slightly. The small intestine is responsible for absorbing the cholesterol from the diet and releasing in into the blood stream. A drug of this type is Zetia (ezetimibe).Possible side effects from this drug can include stomach pain, muscle soreness, and fatigue.
Combination cholesterol absorption inhibitor and statins decreases LDL and triglycerides and increases HDL. A medication would include one such as Vytorin (ezetimibe/simvastatin). Side effects can include stomach pain, fatigue, constipation, muscle soreness, cramps, gas, and abdominal pain.
Fibrates
Fibrates aid in decreasing triglycerides by reducing the liver production of very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and by increasing the speed of triglyceride removal and increase the HDL. Such medications are known as Lofibra (fenofibrate), TriCor (fenofibrate), and Lopid (gemfibrozil). Possible side effects can include nausea, stomach pain, and gallstones.
Niacin
Niacin decreases triglycerides by limiting the liver’s production ability of LDL and very-low-density cholesterol and increases HDL. This drug can be bought over –the-counter and as a prescription. The prescription form has the least side effects. Medications include Niaspan (prescription niacin) and Slo-Niacin (nonprescription niacin). Possible side effects can include facial and neck flushing, vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, gout, peptic ulcers, and high blood sugar.
Combination statin and niacin drugs decrease LDL and triglycerides while increasing HDL. Medication includes one such as Advicor (niacin/lovastatin). Possible side effects can include facial and neck flushing, dizziness, shortness of breath, sweating, chills, and heart palpitations.
Cholesterol medications may affect each individual differently. They are usually tolerated quite well but the effectiveness can be different which each person. These types of medications can effect one’s liver so it is recommended to have regular liver function tests to monitor the liver.

1 Comment
Thank you Kim Wang, I am certainly going to try most of the natural remedies that you recommend – I so want to take charge of my own health, which is deteriorating with age.
Kind regards Linda