The Sambucus, also known as Elder or Elderberry, is the genus of 5 to 30 different varieties of shrubs and small trees. The Elderberry plant is characterized by feathery leaves, and topped off with clusters of white or cream-colored flowers followed by blue, purple, red, or black berries. Sometimes, though rare, the berries can be white or yellow.
Two of the varieties of Elderberry are herbaceous, which means that when they die off, they return to the ground so that there is no visible stump or remains left. The Elderberry herb comes from the berries and flowers of the shrub or Elder tree, and is a medicinal herb native to parts of both the Northern and Southern hemispheres. The berries and flowers from the Elder tree have been used for various medicinal purposes for numerous human ailments throughout history, and that is why they are commonly referred to as “nature’s medicine chest”.
Varieties of the Elderberry Include:
- Southern Elder: Sambucus australis
- American Elder: Sambucus canadensis
- Blue Elderberry: Sambucus cerulea
- Chinese Elder: Sambucus javanica
- Elder or Black Elder: Sambucus nigra
- Madeira Elder: Sambucus lanceolata
- Canary Islands Elder: Sambucus palmensis
- Peruvian Elder: Sambucus peruviana
- Florida Elder: Sambucus simpsonii
- Velvet Elder: Sambucus velutina
The Elderberry Herb throughout History
The Elderberry has been used as an ingredient in wines, marmalades, drinks, and desserts, but it has also been widely used for its medicinal purposes. Juice from the berries was used to relieve colds, influenza, bronchitis, asthma, and other respiratory problems. An infusion of the juice was believed to alleviate inflammation and was therefore used for urinary or bladder infections, back aches, and even nerve problems.

The flower of the Elderberry plant would also be made into creams, washes, or poultices, and used for skin irritants and aliments including, scrapes burns, abrasions, and cuts. The application of the elderberry flower was also used to helped reduce swelling, and inflammation of the skin; and to calm and soothe complexions from the effects of eczema, psoriasis, and acne.
Additionally, an effective eye wash could also be made from the flowers. The various parts of the Elderberry plant that were commonly used included the berries, leaves, flowers, and even the bark.
Elderberry Folklore
Many cultures believed the Elder tree was inhabited by either a witch or elder. A special chant to the elder had to be performed while cutting down an elder tree or it was believed the inhabitant would cause the person harm.
So How Does Elderberry Work?
To understand how the Elderberry works one must first have a basic understanding of viruses and the human immune system. When the immune system is attacked, its first response is inflammation. Inflammation is caused by the increased amount of blood flowing to the body’s tissues. Viruses can only multiply and spread to other cells, by first entering healthy cells. Some viruses enter the healthy cells with help from special spikes called haemagglutinin spikes. Once inside a healthy cell, the virus can then grow and spread, usually resulting in the person exhibiting cold or flu like symptoms.
Antivirin is an antiviral agent contained in the Elderberry. Antivirins work by coating the haemagglutinin spikes of the virus and thereby neutralizing its ability to enter healthy cells. The anthocyanin (a powerful antioxidant) found in the skin of the Elderberry, helps defend the immune system by attacking free radicals in the body.
Free radicals enter the body thru outside contaminants such as pollen, smoke, and other airborne pollutants; once these free radicals enter the body, they being their journey of destruction. Free radicals are molecules that are missing electrons. These molecules invade and steal electrons from other molecules which then sets off a chain reaction of electron stealing, and results in the creation of new free radicals in the body. The multiplying of free radicals leads to cellular destruction and damage, and eventually, inflammation and damage of the arterial wall. This process, and the addition of free radicals in the body, leads to many common diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, diabetes, arthritis, and heart disease, in addition to the general aging of the body.
The human body contains many naturally occurring antioxidants from the production of certain hormones, vitamins, and minerals. Antioxidants work to neutralize free radicals by stabilizing them. Antioxidants give up electrons to free radicals thereby deactivating the free radicals in their electron-stealing mission.
Of all the herbs, Elderberries are ranked third highest in vitamin C content. In addition, they also contain large amounts of vitamins A and B, carotenoids, and amino acids. The skin of the elderberry fruit has the highest concentration of athocyonins of any other fruit. Athocyonins are powerful antioxidants that build and boost the human immune system.
Properties of the Elderberry plant include:
- Vitamins A, B, and C
- Amino Acids
- Carotenoids
- Alkaloids
- Hydrocyanic Acid
- Tinnis
- Free Fatty Acids
- Betulin
- Potassium Nitrate
- Invertin
- Cane Sugar
The Elderberry and Modern Science
Today, Elderberries that are formulated into syrups are effective against, and help to alleviate, the build-up of mucous and calm inflammation in the nasal and bronchial passages and build up the immune system. In 2009, Retroscreen Virology of London tested the Sambucol brand of Elderberry syrup, which is formulated using black Elderberry.
The results of their testing proved the syrup to be 68.3% effective against the H1N1 virus, also known as Swine Flu1. Another study conducted in 2005, found the same brand of syrup to be 99% effective against the H5N1 virus, more commonly referred to as the Avian bird Flu1. Other studies conducted concluded that the syrup was highly effective in the treatment of influenza A and B. Elderberry proved to lessen the amount of discomfort felt by those studied, and symptoms were relieved within 2 to 3 days and at least 3 days earlier than the control group.
The Modern Elderberry
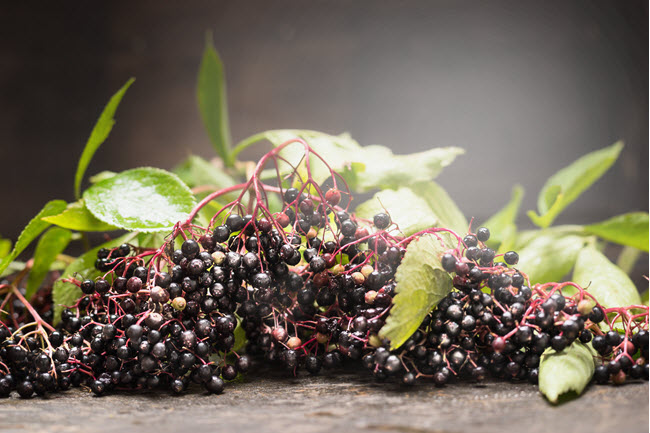

Many people still cultivate and use the Elderberry today. It is still common for Elderberries to be made into pies, jams, jellies, and other sweet desserts. The Elderberry has also been used in alcoholic beverages and soft drinks such as the “Shokata” which was marketed and sold by Fanta in 15 countries worldwide. Elderberry is also widely available to purchase today, and can be used medicinally by adults as well as children.
It can be found in various forms including, liquids, syrups, extracts, pills, capsules, and gummy drops. In some instances Elderberry is combined with Echinacea, goldenseal, and other herbs to help support the immune system, and improve respiratory problems associated with changing seasons and environmental conditions and allergens. Syrups are commonly used to fight off cold and flu like symptoms and support and improve respiratory health and function. The flowers are still used today to make teas and infusions.
Where to Buy Elderberry
Elderberry can be purchased from nearly any local and online health stores, pharmacies and retailers and is available in many different forms and brands. Some of these retailers and online stores are:
- Higher Nature
- Your Nutrition Shop
- Goodness Direct
- Your Health Food Store
- The Nutri Centre
- Nature’s Clock
- Boots
- Holland and Barrett
- The Health Store
- The Nutri Centre
Common Brands of Elderberry
Sambucol produces many varieties of syrups and liquids which include, original, sugar free, children’s, and immune support. In addition, they also offer, cold and flu quick dissolve tablets, and original and immune tablets with added vitamin C. The products range in price from 12.99 for 4fl (120ml) to $29.99 for 7.8fl (230ml).
Gaia Herbs products include: drops, syrups, and capsules, and range in price from 1 oz drops for $7.49 to $22.99 for 5fl (160ml).
Rainbow Light formulates the gummy drops, and can be purchased for $10.99 for a bottle of 30 gummy drops.
Planetary Formula’s syrups range in price from $8.75 for 2 fl. oz. to 27.98 for 8 fl. oz.
Many more brands and varieties can be found and shoppers can even compare prices, brands, and read reviews by shopping online for Elderberry products.
Elderberry Dosages and Interactions
Many parts of the Elderberry plant contain a glycoside which produces cyanide. The cyanide can build up in humans and result in poisoning. For this reason, children were warned against making flutes and whistles from the stems and branches of the shrub, and only ripe berries should be consumed. The flowers can cause gastrointestinal irritation as Elderberry is also a diuretic. As a general rule, there are no known side effects or drug interactions associated with using the Elderberry herb when prepared or formulated properly.
The recommended dosage of the liquid form of Elderberry is:
- For children (1-6 years of age) 1 teaspoon (5ml) per day and can be increased to 1.5-2 teaspoons (10ml) per day, for use during winter months.
- For adults the recommended dose is 2 teaspoons (10ml) per day.
- Other forms can be dosed as follows:
- Dried flowers can be used as an infusion for adults, 3 to 5 grams, three times daily.
- Liquid Extract, for adults, use 1:1 in 25% alcohol, (3 to 5 ml) three times daily.
- Tincture, for adults, use 1:5 in 25% alcohol, (10 to 25 ml) three times daily.
Sources
1. www.sambucolusa.com
2. Answers.Com
3. MedicineNet.Com
4. WebMd.Com