Vitiligo is a condition that occurs when white patches start to appear on the skin. These white patches can vary in their size and location of where they can be found. Melanocytes are pigment cells which produce the pigment melanin.
Melanin is responsible for determining the color of one’s skin, hair, and eyes. The white spots develop when the melanocytes are destroyed and no longer producing melanin. Areas in which pigment can be lost include the areas of the hands, face, and chest; around body openings such as eyes, nostrils, mouth, nipples, belly button, and genitalia; body folds such as arm pits and groin; injury sites of burns, scrapes, or cuts; hair, in which early graying occurs; and in the back of the eye.
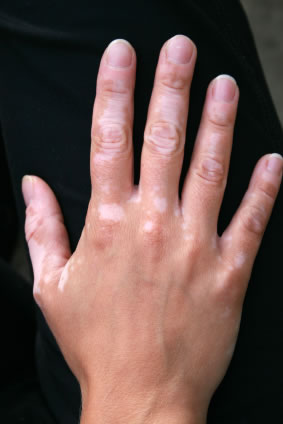
An alternative name for vitiligo is leukoderma. It is a medical term which means white skin and vitiligo is one form of leukoderma. It is also known as ‘white spot disease’ or ‘achromia’, which means loss of color.
Symptoms
The main symptom of the vitiligo skin disorder is the occurrence of rapid pigment loss to the skin, resulting in white patches. This condition can occur in several areas throughout the body. Other signs may include premature whitening of the hair on the scalp, eyelashes, eyebrows, or beard; loss of color in the tissues lining the inside of the mouth; or loss in color of the retina.
The white patches which form on the skin can occur in three different patterns. The focal pattern shows the depigmentation being limited to only one or just a few areas of the body. Segmental patterns shows a loss of skin color only on one side of the body. The generalized pattern has pigment loss widespread over all parts of the body.
Vitiligo has been proven to be associated with other diseases and disorders. Associated skin disorders include ichthyosis, halo naevus, psoriasis, lichen planus, premature graying of hair, and alopecia areata (loss of hair). Systemic disorders which may be associated include thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, System Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), pernicious anemia, Addison’s Disease, Collegen diseases, Grave’s disease, and diabetes mellitus. It has also been noted that many people who have vitiligo are deficient in folic acid, vitamin B12, vitamin C, copper, and zinc.
Vitiligo? Get Remedies Fast!
Causes
There is no real cause or reason as to why one experiences vitiligo. It can involve genetics or immunologic and environmental factors. If one is exposed to the right situation it may increase their chances of this condition. Some may experience vitiligo after sunburn and others may experience it after emotional trauma such as a death, accident, or divorce. Each individual has their own reasons and causes for their development of vitiligo and it is essential for their doctor, the dermatologist, to understand each individual situation in order to prescribe treatment.
The condition of vitiligo occurs when there is a loss of pigment in the skin. This happens when the melanocytes, or pigment-forming cells, are destroyed. This may be due to an auto-immune condition in which the body’s immune system destroys the pigment cells, otherwise known as melanocytes. Or, it could be due to the melanocytes being destroyed by internal biochemical reactions occurring while the melanocytes are making pigment.
Another cause could be that the nerves in the skin are producing signals that destroy the melanocytes. Vitiligo can be caused by one or more of these situations and there is medical treatment aimed at attempting to stop each of these occurrences. There are other treatment options available which try to stimulate the division of living melanocytes and move them to areas of depigmentation.
Risk factors
Two to five million Americans have this condition. Most develop it early in life between the ages of 10 and 30. It affects both men, women and all races equally, though it is more noticeable in people with darker skin.
This condition can be hereditary and families who are associated with it can experience premature graying of the hair.
Those with autoimmune diseases, such as thyroid disease, are at greater risk for this condition.
Patients with vitiligo suddenly have no natural protection from the sun for their skin. Melanin offers protection to the skin from damaged caused by sunlight. Without melanin, there is no protection. The white patches can easily burn, therefore, patients should wear sunscreen with a SPF of 30 on all white areas of skin. Because of this problem, patients with vitiligo are at greater risk for skin cancer and skin aging.
Test and Diagnosis Considerations
Usually a skin examination is all that is needed to diagnose vitiligo. A Wood’s light examination may be done to distinguish vitiligo from other conditions of lightened skin. Due to the fact that there may be other causes of pigment loss, a skin biopsy may be required. Blood tests can be performed to monitor the levels of thyroid or other hormones and vitamin B12 levels. Additionally, an ANA Test (Antinuclear Antibody) may be ordered to help determine if the patient has any autoimmune diseases.
Treatment Options
There is no cure for vitiligo but it can be treated. The goal of treating this skin condition is to stop or slow down the pigment loss. While vitiligo is difficult to treat, there are options available. A simple treatment is to use makeup or self-tanning lotion to camouflage the white spots. Medically, there are two treatment options to consider, repigmentation therapy and depigmentation therapy.
Re-pigmentation Therapy
Repigmentation therapy is the process of trying to restore the normal skin pigment. This is done by creating new pigment cells from already existing ones. These new cells can come from the base of hair follicles or from the white patch itself if depigmentation is not complete. Not all people are good candidates for this type of therapy.
Generally, children and young adults have been known to have a greater success rate. Patients should be healthy and be able to tolerate the long, tedious process involved. It is important to note that if a person has vitiligo over half the body, they are not a good candidate for re-pigmentation.
Hydrocortisone Creams
Hydrocortisone creams can be applied to the skin to slow down the process of depigmentation and to enhance repigmentation. Prescription strength cortisone ointments or creams are required as over-the-counter creams are too weak. Corticosteroids are often considered first in the attempt to treat vitiligo. They may be used topically (applied to the skin) or systemically (ingested/injected into the body). Topical use is considered for small lesions and systemic use is considered for numerous and widespread lesions.
Topical corticosteroids do have some side effects such as thinning of the skin, stretch marks, telangiectasia (dilation of small blood vessels), hypertrichosis (excessive growth of hair), and acneform papules (resembling acne). Systemic corticosteroids are effective in stopping the spread of vitiligo but they do have some serious side effects. They are usually used only for severe cases.
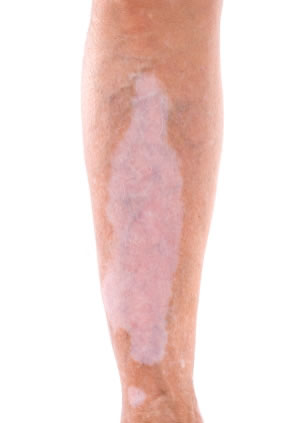
Another type of topical treatment involves a non-steroidal group of immunodulators, such as Pimecrolimus and tacrolimus. This treatment helps to regulate the activity of the immune system and stop the immune system from destroying melanocytes. Potential side effects include a stinging and burning sensation to the skin, but more seriously, these drugs may have some cancer risk associated with them.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy can induce repigmentation. This can be done alone or in combination with hydrocortisone treatment. Therapy of this sort involves narrow-band ultraviolet B light, excimer laser, and PUVA (psoralen plus UV-A). This treatment is considered when topical treatments are ineffective.
- Narrow-band UVB treatment is a new option for vitiligo treatment and involves exposing the skin to a narrow-band UVB light. This process has minimal to no side effects and can be done in a doctor’s office. This procedure requires treatment 3 times a week for several months.
- Home phototherapy units are also available. This treatment is usually considered the first choice for treatment options. Side effects include itching of the skin and redness. Long-term effects include skin cancer and premature aging of the skin.
- Excimer laser treatment exposes the skin to a beam of laser light. This process can only be done in a doctor’s office. It is most often used for small areas of depigmentation and should be used as a complimentary treatment option.
- PUVA therapy involves giving a patient a psoralen drug and then exposing him to UV-A light. Repigmentation is stimulated when this drug is activated by light. The pigment cells are stimulated to move into the vitiligo lesion. There are definite risks to pregnant women and they should not be treated with this procedure due to the harmful effects of the drug on the developing baby.
Depigmentation Therapy
Depigmentation therapy is considered when one wants to try destroying the remaining pigment cells. The process involves removing the normal skin color so it matches the patchy white areas. This is beneficial to patients who have vitiligo over half of the body or more. This treatment involves a topical agent called Benoquin (monobenzylether of hydroquinone). The process requires strict medical attention and does have serious side effects. It is important to note that depigmentation is generally irreversible but occasionally some patchy areas may return.
Remedies and Treatments
Herbal & Home Remedies
The use of herbal remedies should be used with caution in treating vitiligo and they should be used only under a doctor’s supervision. Patients with autoimmune diseases need to be cautious with herbs such as Goldenseal, Astragalus, Echinacea, and Spirulina. These herbs are immune boosters and may boost the body’s destroying of melanocytes.
Pharmaceutical
There are many drugs available to help treat vitiligo. The reason for this abundance is because the condition affects each individual in its own way and, therefore, what works for one person may not work for another. Once an effective medication is found for treatment, it may only work for a little while and the patient will then have to search for other treatment options.
Transplant treatment
Skin transplant procedures seem to look promising for the future of vitiligo treatment. This involves a dermatologist removing a patch of normal pigmented skin and grafting it onto a depigmented area. There is also Melanocytes Transplant Therapy to consider. This involves the dermatologist taking pigment cells from a normal pigmented patch of skin, growing them in a culture, and placing them onto a white patch of skin.
Additional therapies
Therapy from a mental health professional is oftentimes very helpful for patients with vitiligo. Counseling and group sessions can be beneficial to patients when they can talk and discuss their situation with other individuals who are experiencing the same condition. Patients with this disorder often feel anger, embarrassment, anxiety, isolation, and depression. They need to receive positive support from their families and friends, doctors knowledgeable about the disorder and treatment, and they need to find a way to generate positive self-esteem.

1 Comment
please suggest me! how can I remove the spots…. I have no idea please help me..