Respiratory Diseases are ailments and conditions that impair our respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for proper delivery of oxygen throughout the body, removal of carbon dioxide and toxic waste, ample regulation of the body temperature and the stabilization of the body’s pH level. Respiratory diseases are those that affect the lung, bronchial tubes, pleural cavity, trachea, upper respiratory tract and all muscles and nerves involved in the breathing process.
There are many reasons why respiratory diseases occur. They could result from an infection, accident or from inhaling some toxic products. It could also be genetic or a byproduct of unhealthy habits such as smoking. Genetics also play a part in contributing to the occurrence of respiratory diseases.
Types of Respiratory Diseases
There are several types of respiratory diseases. Let us briefly define them and look at some examples of each type.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Lung diseases that result from a severe obstruction of airflow Mto the lung are termed as a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or COPD. These diseases would damage and narrow the airway and block airflow in the lungs.E.g.: Emphysema
Obstructive Lung Diseases
This is a form of lung disease that occurs when the airflow in the bronchial tubes get narrowed, restricting airflow to the lungs.
E.g.: Asthma, Silicosis
Restrictive Lung Diseases
Lung diseases of this form occur where there is a reduction in lung volume either because they cannot stretch enough to alter its volume according to the pressure applied, or due to diseases affecting the pleura or chest wall.
E.g.: asbestosis, Sarcoidosis and pulmonary fibrosis
Respiratory Tract Infections
Upper respiratory tract infection
Essentially, these are infections that occur to the upper portion of the respiratory system. Some examples are common cold, sinusitis, tonsillitis, otitis media, pharyngitis and laryngitis.
Lower respiratory tract infection
The most common example of an infection affecting the lower portion of the respiratory tract is pneumonia.
Respiratory Tumors
Respiratory tumors are either malignant or benign. While the benign ones such as pulmonary hamartoma rarely cause respiratory diseases, lung cancer caused by malignant tumors pose a significant health problem. Lung cancers accounts for 15% of all cancer reports and 29% of all deaths due to cancer.
Pleural Cavity Diseases
Pleural cavity diseases occur when fluid gathers in the pleural cavity during pleural effusion or when a hole in the pleura, called pneumothorax causes the affected lung to collapse.
E.g.: Emphysema and Mesothelioma
Pulmonary Vascular Diseases
Diseases are regarded as pulmonary vascular diseases when they impact the pulmonary circulatory system of our body. They could occur from a pulmonary embolism, pulmonary arterial hypertension, pulmonary edema and damage to the capillaries in the lung that results in blood leaking into the alveoli.
Symptoms
Respiratory diseases can be detected with some of these many symptoms. One should definitely seek medical consultation and help if they find themselves suffering from one or more of these symptoms.
- Shortness of Breath with or without exertion
- Breathing Difficulties or Dyspnea
- Rapid Breathing
- Dizziness and Fainting
- Chest Pains
- Accelerated Heart Rate of more than 100 beats per minute. This is also known as Tachycardia.
- Fatigue
- Loss of Appetite
- Weight Loss
- General uneasy feeling
- Bluish discoloration of the lips, tongue and/or fingers, also known as cyanosis.
Risk Factors
There are many factors that could contribute to the increase in occurrence of respiratory diseases. Constant exposure to these factors could increase the chances of respiratory diseases occurring.
- Tobacco smoke
- Indoor air pollutants such as those that could come from open stoves, mold, dust mites, and pollen.
- Outdoor air pollutants that can arise from exhaust fumes from cars and factories, smoke, dust and smog.
- Allergens that can comes from pets, pollen, dust mites, mold, smoke, formaldehyde and volatile organic Compounds (VOC).
- Occupational hazards such as exposure to toxic fumes, chemicals and harmful substances
- Unhealthy Lifestyle such as smoking.
Tests and Diagnosis
To determine if one is suffering from any type of respiratory disease and to determine which type, several tests could be ordered by the physician. The type of test that would be administered on a patient depends on their medical history, family history, symptoms and the diagnostic procedure physicians are expected to follow.
Some of the tests are
- 1. Chest X-Ray
- Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs)
- Computed Tomography Scan
- Examination of microorganism cultures derived from secretions like sputum
- Bronchoscopy
- Biopsy of the lung or pleura
- Ventilation/Perfusion Lung scan (V/Q lung scan)
- Ultrasound
Chest X-ray is a radiograph projection of the chest that helps physicians analyze and diagnose respiratory diseases. It uses ionizing radiation to create images of the chest. X-rays are used to determine conditions that involve the chest wall, thorax bones, lungs and heart. The occurrence of pneumonia is commonly determined through an X-ray.
The most common PFT that is used to measure lung function is spirometry or the measurement of breaths. This is a tool that is used to create pneumotachographs that can be used to determine respiratory conditions like asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Also known as a CT scan, this is a medical imaging procedure that uses tomography to create a three-dimensional image of the body part. High resolution computed tomography scan is used to diagnose respiratory diseases like emphysema and fibrosis. A general purpose image reconstruction technique is sufficient to check for pneumonia and cancer.
A microbiological culture is created when microbial organisms are allowed to multiply in a controlled environment and then tested to determine the cause of an infectious disease. In some cases, a chemical test is conducted on the culture to determine and eliminate certain causes of infection or diagnosis and could be vital information to determine the form of treatment that needs to be administered to the patient.
This technique allows the insides of the airway to be viewed. Bronchoscopy also helps to provide therapeutic relief. The bronchoscope is inserted into the airway through the nose, mouth or a tracheostomy. It helps physicians analyze the airways for abnormalities like blood, tumors and inflammations.
This medical test involves the examination of cells or tissues that are removed from the patient. These are examined through a microscope by a pathologist and could be chemically analyzed.
This form of medical imaging that uses scintigraphy to assess the blood and air circulation within the lungs. The ventilation part of the scan allows on to determine how air reaches all parts of the lung and the perfusion part assesses how blood circulates within the lungs.
Ultrasounds are especially useful to determine the effect of pleural effusion. Pleural effusion occurs when excess fluid gathers in the pleural cavity of the ling. This could limit the expansion of the lungs and affect their breathing ability. The four types of fluid that could accumulate and cause pleural effusion are serous fluid, blood, chyle and pus.
These tests would help determine the exact type of respiratory disease that has occurred and would allowed doctors to determine the type of treatment that needs to be administered.
Treatment Options
Many factors affect the type of treatment that would be administered for respiratory diseases. These factors are the type of respiratory disease, its intensity and the medical history of the patient in concern. Here are some possible treatment options that would be suggested to help manage one’s respiratory disease.
- Medication
- Physiotherapy
- Oxygen Therapy
- Mechanical Ventilation
- Radiotherapy
- Surgery
Patients could be prescribed with corticosteroids, bronchodilators, antibiotics, anticoagulants, cancer chemotherapy and immune suppressants to help them with their respiratory diseases.
Side effects of these medications vary from one medicine to another. All patients must ensure that doctors know their full medical and family history to determine which form of medication is the safest and would be most suitable for them. Patients would also be warned of any specific side effect that could occur from the consumption of the medication and they should understand them clearly and comply as needed. Cost of these medications would vary based on the location, availability of medical facilities and how the insurance of the patient covers the medicinal cost.
Physiotherapy is most used when one has had a pulmonary surgery or has been diagnosed with cystic fibrosis, COPD or pulmonary fibrosis. Physiotherapy helps clear lung secretions and certainly help those who have suffered from respiratory diseases.
This is helpful when one is unable to inhale in sufficient oxygen due to the respiratory disease that their body is suffering from.
This form of treatment is primarily administered when patients suffer from emphysema, pneumonia and any respiratory disorder that impacts the oxygen intake of the body.
This form of treatment is flexible and can be administered in the hospital, at home and could be made portable as well.
This process involves the mechanical replacement of the natural breathing process with ventilators. This method involved a ventilator and a trained individual who compresses the bag as required. This could be used as a short term measure during an operation or for chronic illnesses as well. Possible side effects are complications such as pneumothorax, injury of the airways and alveola, and ventilator associated pneumonia.
This process utilizes high energy rays to kill some or all cancer cells. In early stages of cancer, it could completely remove the cancer. In other cases, it can be supplemented with chemotherapy or surgery. In more advanced lung cancer, radiotherapy treatments could keep the illness under control by shrinking the cancer cells, providing some symptomatic relief for the patient.
Surgical procedures like lobectomy and pneumonectomy could be performed to remove the cancer. Pleurodesis is a procedure that artificially eliminates the pleural space. Lung Volume Reduction Surgery where the damaged portions of the lung could help with COPD and emphysema patients. A patient’s damaged lung could be partially or completely replaced through lung transplantation. Surgery also allows for an artificial lung to be implanted into the body.
Home Remedies to Treat Respiratory Diseases
While there are many treatment options, there are some natural home remedies that one could take to control their respiratory diseases. These natural remedies could be consumed to provide relief from the symptoms of the respiratory diseases, cure the diseases to some extent and keep them in control. Needless to say, these natural remedies do not replace the doctor’s advice and prescription. When one intends to undergo a strict natural regimen, they should consult their doctor and do it as a supplement to the medications and treatments that is being administered to them.
Ginger
Ginger is a perennial herb that belongs to the rhizome family. The medicinal values possessed by gingers have been recognized for a long time by ancient Indians, Chinese and Greek physicians. Ginger is also used as a spice in many cultural dishes. The vitamins and minerals found in ginger are phosphorus, calcium, iron, carotene, thiamine, vitamin C, niacin and riboflavin. Ginger provides a great remedy for coughs and colds. When consumed with honey, ginger could provide relief from dry cough. Ginger tea is also a great remedy for colds and fever.
Fever resulting from influenza could be reduced from a mixture consisting of ginger juice, fenugreek and honey. It also works as an expectorant in asthma, bronchitis, whooping cough and tuberculosis.
Chicory
Chicory is a perennial herb that has long tap roots, round stems and several light or dark green leaves and pale blue flowers. This herb is native to the Mediterranean region and was known to the ancient Greeks and Romans. Its ability to create better skin was discovered a long time ago. Chicory is helpful for asthma and hay fever recovery. Juices of chicory, carrot and celery after eliminating starches and sugars help with these respiratory conditions. Powder derived from the dried chicory roots mixed in honey is a great remedy and expectorant for chronic bronchitis.
Celery
This salad plant consists of green leaves, stem and bulbous roots. The celery roots and seeds are popular in Unani and Ayurvedic treatment and medicines. The Chinese and English have used celery as a medicine since the fifth century B.C. Celery contains a well balanced proportion of nutrients, vitamins and minerals. Its antispasmodic properties help in treatment of respiratory diseases like asthma, bronchitis, tuberculosis and pleurisy.
Tumeric
Tumeric is a perennial herb that has short stems and raised branches. This rhizome has been used by those who practice Unani and Ayurvedic medicine since ancient times. The antiseptic properties of turmeric make it a good remedy to treat chronic cough and infected throats.
When fresh turmeric powder is mixed in warm milk, they make a good remedy concoction that would help increase the discharge from the nose and provide relief from cough and cold. It is also used as a great in house remedy for bronchial asthma.
Prevention Tips
One could prevent the occurrence of respiratory diseases by adhering to at least some of the prevention tips that are mentioned here. While these prevention tips may not entirely eliminate the chances of suffering from a respiratory disease, they would at least reduce the chances of respiratory diseases from occurring. It could also help with the healing process and ensure that the infectious respiratory diseases do not spread across the population. These measures are also good for general health of all within the family and society.
- Do not smoke. If you are, work on quitting soon. Smoking would damage your lungs and the lungs of those surrounding you, especially close family and friends. Smoking is the primary cause for many respiratory diseases and you and your loved ones are succumbed to.
- Educate the young children about the hazards of smoking. It would be better to educate them at an early age to ensure that they can stay protected from this unhealthy habit and protect their lung health.
- Avoid inhaling second-hand smoke. Being a passive smoker by inhaling smoke also affects your lungs and increases your chances of being affected by a respiratory disease.
- Be more proactive and protect your family from passive smoking. You could divert from smokers who are in your way. You could also instruct visitors to your home that smoking would not be tolerated.
- Always be clean and thoroughly wash your hands. Fight germs by maintaining your hygiene. The spread of infection reduces when everyone does their part to remain clean and germ free.
- Cover your coughs and sneezes to prevent the spread of flu, cold and other lung diseases.
- Contribute to limiting outdoor air pollution. Do your part to ensure that everyone breathes in cleaner air.
- Find out how you could reduce the amount of indoor air pollutants within your house.
- Ensure that you exercise regularly to build stronger lungs and immune system.
- Avoid occupational hazards such as inhaling toxic fumes from chemicals, paints and other solvents. If needed wear a protective mask and ensure that good air quality is maintained at your work place at all times.
- Ensure that you have taken the necessary vaccinations to protect yourself from respiratory diseases that are prevalent in your area.
Conclusion
Respiratory diseases come in many forms and severities. Learning more about them, how they occur, how they can be treated and prevented would certainly help us manage our lung health better. This is vital information whether you or a loved one is currently managing a respiratory disease.

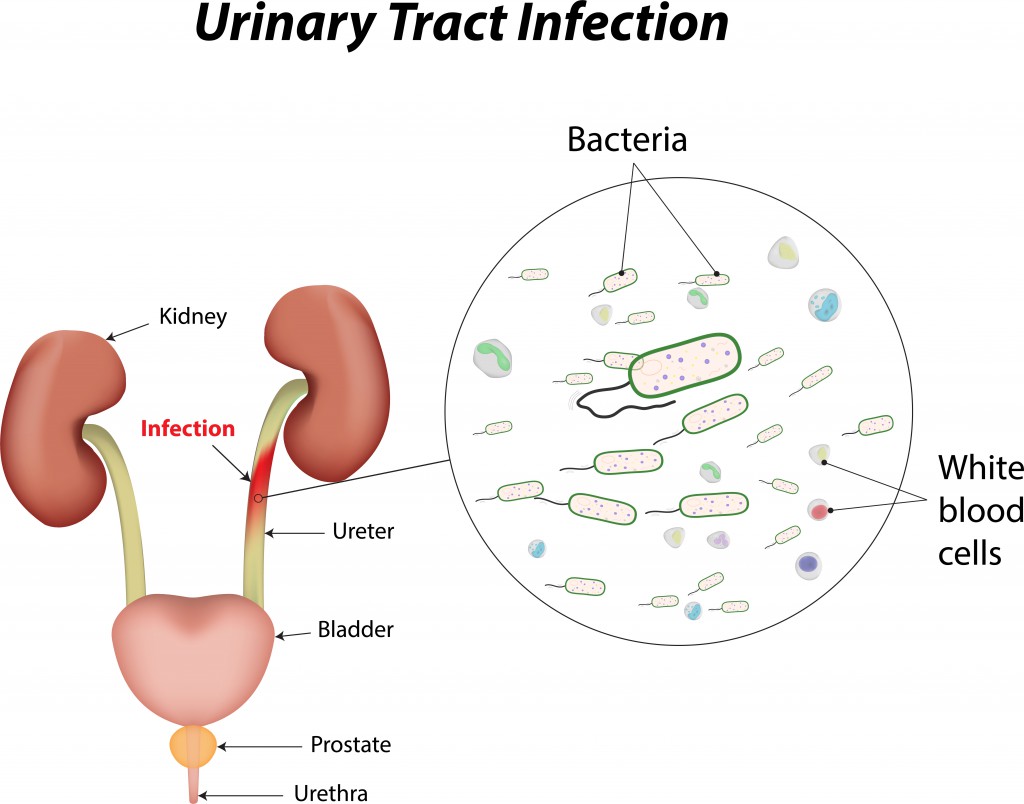
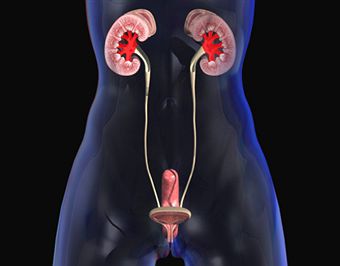 Urinary tract infections usually occur when germs or bacteria somehow enter the urethra and continue through the urinary tract by multiplying. The multiplying of the bacteria can cause an infection in areas of the urinary system. One specific type of bacteria that can cause urinary tract infections is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which can be found normally in the gastrointestinal tract.
Urinary tract infections usually occur when germs or bacteria somehow enter the urethra and continue through the urinary tract by multiplying. The multiplying of the bacteria can cause an infection in areas of the urinary system. One specific type of bacteria that can cause urinary tract infections is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which can be found normally in the gastrointestinal tract.
 There are several over-the-counter solutions to pain and burning during urination available at large pharmacy chains like CVS or Walgreens and local pharmacies.
There are several over-the-counter solutions to pain and burning during urination available at large pharmacy chains like CVS or Walgreens and local pharmacies.