Osteoporosis
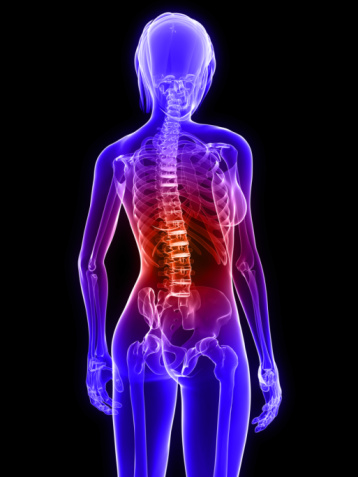
Osteoporosis is a common disease found in elderly adults. It is a disease of the bones that causes them to become fragile and brittle, easily broken and fractured.
This can be life threatening in older adults with their risks of health impairments and already having various impairments.
The density of the bone decreases and they become weaker and more prone to severe injury.
Osteoporosis can cause the bones to become abnormally porous, able to be compressed much like a sponge.
Normal bones are given their strength through a composition of protein, collagen, and calcium.
When Osteoporosis develops, these bones lose this composition and become porous, easily broken with the slightest injury that typically wouldn’t be strong enough to cause any type of fracturing.
This can occur in the hips and ribs frequently in the elderly and cause debilitating disability. In medical terms, with Osteoporosis, bone mineral density, or BMD decreases, allowing bone microarchitecture to be disrupted, changing the amount and variety of various proteins within the bone.
Osteoporosis is caused later in life, more often in women after menopause, yet still apparent within men. There are various causes, some that are attributed to diseases, medications, hormonal deficiencies, and some even diet-related.
There are various treatments used in order to provide better bone mass and improve the symptoms allowing the bones to gain some strength back and prevent the risk for severe injury. Quite often, Osteoporosis is seen as shrinking and slouching of the elderly body, and the decreased use and strength of the limbs.
There are many agencies that assist senior citizens in receiving care and assistance with osteoporosis as it can be quite difficult to manage without the appropriate health care. Family history can have an effect and the treatments chosen are likely to only provide relief and short term effects, more so than long term effective solutions. The best treatment is to prevent osteoporosis using the suggestions of physicians.
Symptoms
The earliest stages of osteoporosis show no symptoms. This doesn’t mean that it isn’t developing, which is why all elderly citizens are suggested to use preventative measures when aging begins to reach the later stages. When women reach menopause they are prompted to seek advice from a health care professional. The earliest stages are silent and run the course without any indication of a situation. It usually isn’t found until there is a bit of pain or a shrinking or slouching effect beginning.
Late Symptoms
The late stages of the disease present several symptoms including bone pain and tenderness as well as fractures from slight force. The first indication of the disease could be seen from an accidental fall that causes a bone fracture that is uncharacteristic for the type and force of the injury.
This gives many physicians the clue that there is an issue with bone mass and it could be linked to osteoporosis. The later stages of osteoporosis could also cause a severe loss of height through time, with as much as a six inch difference.
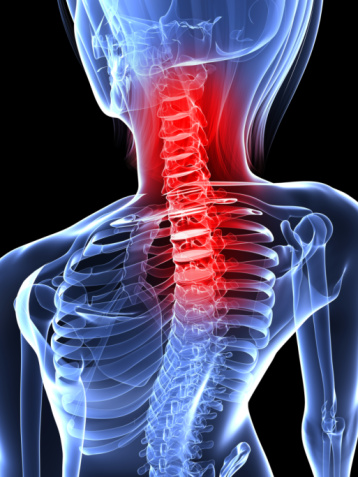
Low Back Pain
Low back pain can become severe and prevalent, as well as neck pain, which is all caused by tiny fractures of the spinal bones. Dowager’s hump is another condition that signifies osteoporosis and is the stooped posture that is signature of the disease.
Osteoporosis can remain a dormant disease for decades as there are no real symptoms until there are the first bone fractures that begin to continue and increase in severity.
Some of these fractures can even go without notice for years as the fractures can be very miniscule and not cause any significant pain or sensation. When fractures of the spine, or vertebra, occur, there are various symptoms such as band-like pain from the back out to the sides, as well as curving of the spine and loss of height.
Causes
There are several different causes of osteoporosis. Many of these causes are hereditary or even stemming from an imbalanced lifestyle.
There are various causes that are beyond your control, including
- Family medical history
- Gender of the individual
- Ethnic origin of the individual
- Family medical history can be a strong influence in your chances of developing osteoporosis.
Seen as a hereditary affliction, the instance of family members with osteoporosis could be a strong causing factor of the disease. There are various hormonal disorders that can actually cause osteoporosis by inhibiting the appropriate build of bone mass.
Osteoporosis is even seen to be caused by some medications including glucocorticoids. When this is the cause, the osteoporosis is termed steroid or glucocoricoid-induced osteoporosis.
Other Causes
Another major cause of osteoporosis is parathyroid gland disease, or hyperparathyroidism. This is a main cause of severe, young adult, or male gendered osteoporosis. It is a fairly easy cause to determine due to the untypical demographic affected.
Over excessive consumption of the dietary protein can also cause the disease, but is often ignored as a cause my many. When too much protein is consumed, calcium is stripped from the bones and expelled within the urine.
There are also several other causes of the disease such as
- Malabsorption
- Poor nutrition and health
- Low testosterone levels within males
- Chemotherapy causing early menopause
- Amenorrhea in young women
The various causes can differ and are often signified by those that are afflicted, as well as the severity of the disease. With males being less affected than women, it is an easier task to determine the cause when men are affected.
Risk Factors
One of the largest risk factors is being a female. Another is being a female going through menopause. With a family history of menopause, there is an even greater risk of about 25 to 80 percent. The actual risk factors of osteoporosis are non-modifiable and modifiable.
There are also various diseases in which osteoporosis has been identified as a side effect or complication associated with either the actual disease or its treatments. Men with a decrease in testosterone levels have a significant risk of developing the disease as well. Thos with a higher risk due to ethnicity are those of European or Asian descent.
Modifiable factors are those that can be changed or are causing osteoporosis as the individual encounters the risk willingly. Such causes include excess consumption of alcohol. This means consuming over three units of alcohol each day, especially when of a younger age.
This increases the risk for these individuals as they get older and aren’t building up the bone mass needed for a healthy structure. Vitamin D is another modifiable risk factor that can be avoided with the proper diet. Tobacco smoking and malnutrition are two more causes that contribute to the decrease in the development of bone mass.
Other risk factors include:
- High protein diets
- Underweight or inactive adults
- Excess physical stress
- Heavy metals including lead
- Sodas and caffeine-not highly supported
There are various medications as well such as long term use of heparin, phenytoin, or prednisone. These medications may be needed to combat other ailments and cannot be modified in some cases, however if there are medications that can increase the risk they should be discontinued if allowed.
Prevention Tips
There are several methods that can be taken as preventative measures to protect from the development of osteoporosis. These methods include lifestyle changes and medications. Avoiding an unhealthy diet or the overconsumption of protein, refraining from smoking, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption can be great at preventing osteoporosis.
Exercise is also an effective prevention measure as there can be a bone density decrease without the proper exercise if there are other risks for osteoporosis present. Walking, jogging, as well as stair climbing with 70 to 90 percent of the maximum effort exerted at least three times per week has been shown to have a five percent increase in the bone density over 9 months. This can be an excellent method of preventing the disease from progressing or presenting health risks.
Any diet that is high in calcium and vitamin D will greatly prevent the occurrence of osteoporosis, offering a strengthening factor of the bone and an increase in bone density development. Combined, they are perfect for preventing bone fractures and are a low cost choice for prevention. Calcium carbonate is less expensive than calcium citrate, but the more expensive type can be much more effective and can even be taken without food.
SERM
Various medications prescribed to assist in the prevention of osteoporosis including a SERM, selective estrogen receptor modulator, raloxifene. Although estrogen replacement therapy has shown to be highly effective in prevention of osteoporosis, it is rarely recommended without various other indicators. For this reason, it is typically given to those that are the greatest at risk and the furthest from menopause at there has been some concern over the use of estrogen in women during the first decade after menopause has occurred.
Test and Diagnosis Considerations
In order to diagnose osteoporosis, a bone mineral density test will be performed, usually in the form of a densitometry or what is called a DEXA scan. This will measure how much bone is present compared to the normal amount. This will be used to predict any risks of future bone fractures due to the disease. There is also a spine CT scan that will show any loss of bone mineral density. In some rare cases, a QCT, or quantitative computed tomography will be used.
There are more severe cases in which a spine or even a hip X-ray may be necessary in showing the bone fractures or any collapse of the spinal bones, but this type of exam is ineffective at diagnosing or predicting whether or not someone has osteoporosis. If the osteoporosis is linked to any type of medical condition, there may be blood and urine tests that will identify any type of disorder.
Increased Mortality
Patients that are diagnosed with osteoporosis are more likely to have an increased mortality rate because of complications due to a fracture, however most patients don’t die from the disease, simply with it. If a hip fracture occurs, there can be various effects such as decreased mobility and other complications like a pulmonary embolism or even pneumonia.
There is an approximately 13.5% six month mortality rate that follows any hip fracture. Vertebral fractures don’t affect the mortality as much, however can cause severe chronic pain that is hard to manage, and even deformity in the patient’s form. Quality of life is severely impacted by osteoporosis, not allowing appropriate mobility and function.
Treatment Options
There are various objectives of osteoporosis treatment including controlling pain associated with the disease and slowing the progression of the disease. There are also treatments aimed at preventing any type of bone fractures by strengthening the bone.
A more comprehensive and physical treatment is aimed at preventing the risk of falls that are known to cause severe fractures in those affected by osteoporosis. There are several lifestyle changes and medicines that are used in order to treat and manage osteoporosis most effectively. Various newer alternative treatments are experimented and attempted showing differed effectiveness.
Herbal and Home Remedies
There are a great deal of natural and home remedies for osteoporosis, many proving to be quite effective in treating and assisting with the treatment of the disease. Such remedies include common bone building exercises. There should at least thirty minutes of some sort of weight bearing exercise like walking, jogging, and running, at least three times weekly.
This is a proven treatment that increases bone density significantly and can increase the progression and combat the disease. Water walking is a great idea for at about thirty minutes, three times weekly, as it is seen to support the body’s weight, decreasing joint pressure, but also providing the same effective bone strengthening.
Dandelion tea is made from the dandelion leaf and has been shown to promote the building of bone density. Increase Soy intake can assist in balancing the estrogen levels within women. There should be consumption of at least 40 mg each day of soy isoflavone supplements.
Chaste berry has also been shown to provide a hormone balance with the vitexicarpin and vitricin content. Taking 250 mg of the extract each day for two to three months can show a significant improvement.
Common Remedies
More common remedies are increasing calcium and vitamin D within the body to promote better bone density and a strengthened bone support, preventing the occurrence of fractures. The introduction of wholesome foods like Brussels sprouts and other vitamin K, and D rich foods, as well as those rich in calcium are quite essential to building and promoting healthy bones.
Medical Treatments
There are various medications used to treat the disease and appease the symptoms of osteoporosis. Such medications include bisphosphonates which are the primary medications used in postmenopausal women to treat and prevent the disease.
There are oral and intravenous medications with the oral medications the most commonly prescribed including
- Fosamax
- Boniva
- Actonel
- Calcitonin is another medication used and has shown effective in decreasing bone loss rate and relieving the pain associated with the disease.
There are side effects such as nasal irritation and nausea. The two main types of this medication are seen in nasal spray and injectable form but is shown to be less effective than bisphosphonates.
Hormone replacement or estrogen replacement therapies are sometimes used, but less often than others as they aren’t approved for treating women that have already been diagnosed with osteoporosis. If the treatment proves successful and there is no reaction to other forms of treatment, physicians may recommend continued use, otherwise it is a rare medical prevention method. There are various risks including infections and underlying health effects.
Parathyroid hormone treatments on the other hand are approved treatment for postmenopausal osteoporosis in women that are experiencing a severe form of the disease and have a higher risk of fractures. Teriparatide, or Forteo, is used through daily shots that are administered under the skin and can be taken at home. There are also other forms of hormonal treatment that are used to treat the disease.
Surgery
Surgery for osteoporosis isn’t possible as there can be no increase to bone mass density through surgical measures, however there is a vertebroplasty that is used to treat small fractures that may be present along the spinal column.
This surgery is also used to prevent week spinal bones from being fractured as the various bones strengthen as this can be a slight risk. There will be a type of fast-hardening glue injected into the fractured or week areas of the vertebrae, which is similar to kyphoplasty that uses balloons in order to spread the spaces for the glue.
Osteoporosis can be a very debilitating disease in that it restricts mobility and severely compromises the quality of life for those affected.
With women being a main candidate for osteoporosis after menopause, it is encouraged that they take much more care of their bones and ensure they live a life that includes healthy choices in diet and exercise, promoting the bones to develop strong and structured.








 There are many herbal solutions to snoring. One of the most common herbs is household ginger.
There are many herbal solutions to snoring. One of the most common herbs is household ginger.